Recent Trends
The surge in infostealer malware has led to an alarming increase in credential compromise, significantly impacting both individuals and organizations. With threat actors exploiting password managers and targeting remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools, it’s crucial to stay informed about these threats.
We’ve reported before about the rise and risks of infostealer malware, and the resultant flood of compromised credentials still shows no sign of abating. In the past week alone, we picked up over 500 million lines of compromised credentials from threat actors and access brokers. Infostealer credentials come primarily from browser-based password managers, so the exact URL where the credential can be used is included with nearly all of this data. This makes it extremely low-effort for threat actors to effect account takeover, and focus their activity on whatever endpoints they are most interested in- for example, a cloud provider like Snowflake, or any other service that users might be logging into.
In last month’s Threat Hunting Report from CrowdStrike, they noted that
“…adversaries still frequently rely on previous reliable techniques, including leveraging legitimate RMM tools for illicit activity. To evidence this trend, over the past 12 months, CrowdStrike OverWatch observed a significant 70% year-over-year increase in incidents leveraging RMM tools” (pg 31).
Remote Monitoring and Management tools are typically used by IT professionals (e.g. managed service providers) to login to customer or employee machines remotely to assist them or perform maintenance. This type of access is naturally extremely attractive to threat actors, who can use the software as a cloak of legitimacy to avoid detection and often obtain very privileged user roles. Without extensive and detailed forensic data, it’s difficult to unequivocally confirm how threat actors are obtaining the credentials to these systems, but we certainly have observed many credentials for the most popular RMM systems in infostealer data as we process and clean it.
For example, CrowdStrike’s report indicates that ‘Connectwise Screenconnect’ and ‘Anydesk’ are the two “most observed RMM tools for illicit activity.” Taking a typical file of infostealer data, we can quickly search for these services’ web endpoints, and results turn up immediately:
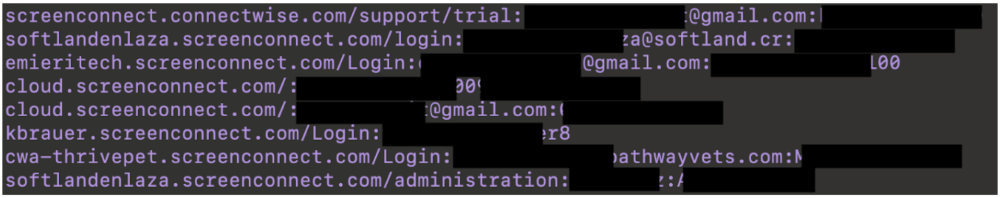 Small sample of compromised credentials for the web endpoints of the Screenconnect RMM service (PII redacted)
Small sample of compromised credentials for the web endpoints of the Screenconnect RMM service (PII redacted)
 Small sample of compromised credentials for the Anydesk RMM service web endpoints (PII redacted)
Small sample of compromised credentials for the Anydesk RMM service web endpoints (PII redacted)
The availability of this data is certainly a huge risk for exposed corporate clients of these services, not to mention any individual users who may have re-used the same password on other websites or services, or clients of the vulnerable companies who may ultimately suffer the effects of a data exposure. Proactive strategies like compromised credential monitoring can detect vulnerable accounts early, allowing organizations and individuals to take immediate action. Staying informed and vigilant is key to mitigating the risks associated with credential compromise.
1. What is infostealer malware and how does it lead to credential compromise?
Infostealers are a kind of malware-as-a-service (MaaS) that exfiltrate data from infected computers to a central server, which is then sold and published as “logs”- comprehensive profiles of the data from each compromised computer. The stolen data comes primarily from the ‘autofill’ and password managers in the user’s web browsers, but stealers also grab files from the Desktop and Documents folders, browser cookies, cryptocurrency wallets, and information from other services like VPNs, Discord, or Telegram if they are installed on the system. These stolen credentials and other data can then be sold or shared on the dark web, within hacker communities, or on known cybercrime communication platforms.
2. Why is compromised credential monitoring crucial for preventing account takeover?
Compromised credential monitoring involves scanning dark web marketplaces, cybercrime forums, threat actor communication platforms, and other sources for stolen credentials. With active, real-time monitoring, organizations can quickly identify if their credentials have been compromised by infostealer malware or in a data breach, allowing them to take immediate action to secure accounts and prevent unauthorized access.
3. How does infostealer malware impact remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools?
Infostealer malware can harvest login details for remote monitoring and management tools like ConnectWise ScreenConnect and AnyDesk. Attackers use these credentials to gain unauthorized access to systems, posing significant security risks.
4. Are password managers safe from infostealer malware?
Browser-based password managers like those integrated within Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Brave, etc, are highly vulnerable and indeed one of the main targets of infostealer malware. These password managers work by storing your passwords in cleartext (i.e. without any encryption) on your computer, which means they can be copied and exfiltrated if your computer is compromised. Web-based password managers like LastPass or 1Password are not directly compromised by infostealer malware, but if you save your master passwords in a browser-based manager, hackers could then obtain your master password using an infostealer.
5. How can organizations protect themselves from credential compromise due to infostealer malware?
Organizations should educate employees about cybersecurity practices, such as avoiding password reuse and identifying malware sources like phishing emails. Organizations should also implement compromised credential screening or compromised password screening, multi-factor authentication, and NIST compliance.
AUTHOR
 Dylan Hudson
Dylan Hudson
Dylan leads the Threat Research team at Enzoic, developing and implementing cutting-edge threat intelligence infrastructure to help protect users and organizations from cyberattacks. When not at work, he can be found hiking and biking in the Rocky Mountains or playing traditional Celtic music on various stringed instruments.
Free for up to 20 users. Save hours of admin time and simply get started.