Credential stuffing is the automated use of collected usernames and passwords to gain fraudulent access to user accounts.
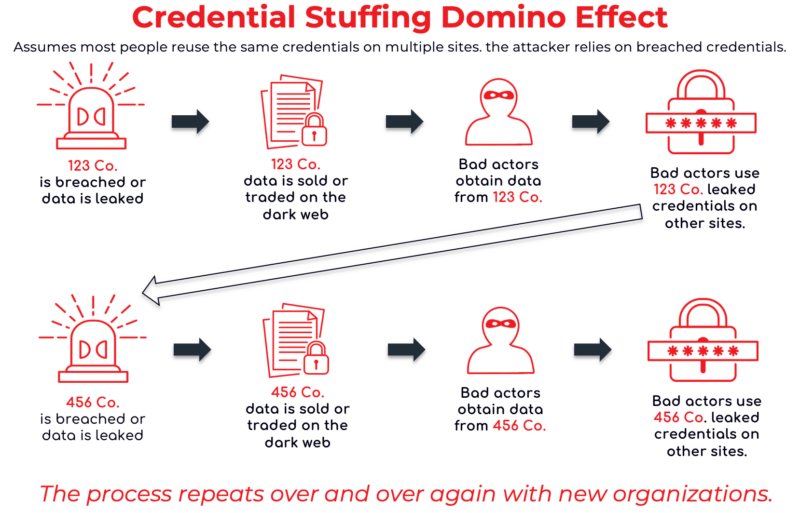
Credential stuffing is a cybercrime technique where an attacker uses automated scripts to try each credential against a target website. It is considered a subset of brute force attacks. The reason this works is the majority of users reuse the same credentials on multiple accounts. This unfortunate reality means one data breach can threaten many organizations.
Credential stuffing is a volume-based attack that lets an attacker have unauthorized access to an account. Once inside, they may do all sorts of things, one of which would be getting access to all users’ data. If that occurs and the data includes credentials, you could say there was a credential spill.
A threat actor compiles or obtains a list of credential pairs (e.g. an username and associated password) typically thousands of entries long at least from a third-party site. It “works” because many people will have reused the exact same credential on the target site. They choose a target, often a login form on a particular website, and run a program that attempts to log in to the website (or other target) with each credential pair.
Cybersecurity research indicates about 1% of stuffing attempts are successful. As the number of attempts is in the billions per year, even a 1% rate means that tens of millions accounts are taken over every year. Also, even a single success means that a threat actor could potentially gain access to the entire system or network through lateral or escalatory movement. This is a known path for the deployment of ransomware and other common cybercrimes.
Verizon DBIR 2021 stated breach data showed that 61 percent of breaches involved credential data and indicates that businesses surveyed across every industry experienced a median of over 1 million credential stuffing attempts during the past year.
There are multiple ways to try to detect an attack.
A primary defense is to ensure the use of unique passwords for each site. Make sure passwords were not previously compromised and continue to monitor credentials on an ongoing basis in real-time to ensure user login credentials have been compromised.
Also, conduct security awareness training for employees on password hygiene and password reuse. Password reuse is what enables attacks so this practice should be strongly discouraged, both at work and at home.
Read 8 Ways to Mitigate Attacks
Credential stuffing is a method of active attack by threat actors. A data breach is a result of the exposure of confidential information; this can occur through error, lack of responsibility and security of an organization, or any other different cyberattacks.
SOO reduces the chance that a user’s credentials would be exposed in a breach incident because it reduces the number of “doors”/entry points that an organization needs to make secure. However, it becomes even more integral that the main account used for SSO has a strong, unique, and uncompromised password.
Additional articles: